
Are you worried your dog might be too heavy? Obesity in dogs is a big health problem in the United States. Knowing about canine obesity can help you keep your dog healthy and happy!How can you tell if your dog is overweight? Weight issues aren’t just about looks. They can really hurt your pet’s life and health. Our guide will teach you all about managing your dog’s weight and making their life healthier Obesity In Dogs .
Dogs come in all sizes, but they all need to stay healthy. Obesity can cause many health problems. These problems can shorten their life and make it hard for them to enjoy everyday activities.
Key Takeaways
- Canine obesity is a widespread health issue affecting many dogs
- Extra weight can seriously impact your dog’s overall health
- Early detection and intervention are critical for weight management
- Diet and exercise play a key role in maintaining a healthy weight
- Professional veterinary guidance is essential for safe weight loss
Understanding Canine Obesity: A Growing Health Crisis

Pet obesity is a big worry for dog owners in the United States. Our furry friends are facing serious health issues because of too much weight. Facts about dog obesity show a worrying trend that affects their health and how long they live.
Defining Obesity in Obesity In Dogs
To fight dog obesity, we need to know what makes a dog overweight. Vets use a body condition score to check. Dogs are obese if they are 20% or more over their ideal weight.
- Normal body weight ranges vary by breed
- Body condition scoring helps identify excess weight
- Professional assessment is key for accurate diagnosis
Current Statistics on Obesity In Dogs
Recent studies show scary stats on obese dogs. About 56% of dogs in the United States are overweight or obese. This problem affects dogs of all ages, breeds, and sizes.
| Dog Weight Category | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Overweight | 40% |
| Obese | 16% |
Impact on Pet Longevity Obesity In Dogs
Too much weight greatly shortens a dog’s life. Overweight dogs live 2-3 years less than healthy ones. The extra weight is hard on their joints, heart, and metabolism.
Maintaining a healthy weight is key to ensuring your dog’s long and happy life!
Is Your Dog Overweight? Here’s All About Obesity In Dogs, Obese Dog Weight Loss

Wondering if your furry friend might be carrying extra pounds? Figuring out if your dog is overweight can be hard. But don’t worry, we’re here to guide you through dog weight management with ease!
Vets use a few key ways to check if your dog is overweight. They look and touch to get a clear picture. Is your dog overweight? Let’s find out!
- Visual Body Check: Look at your dog from above and from the side
- Feel the Ribs Test: Gently run your hands along your dog’s sides
- Waist Definition Assessment: Check for a visible waistline when viewed from above
Professional weight management for obese dogs begins with understanding body condition. Dogs at a healthy weight should have:
- Visible waist behind the ribs
- Ribs that can be felt without excessive fat covering
- Minimal abdominal fat
Pro Tip: If you can’t easily feel your dog’s ribs or notice a significant layer of fat, it might be time to consult your veterinarian about a weight management plan!
Each dog breed is different, so what looks like a healthy weight can vary. Small changes in diet and exercise can make a big difference in your dog’s overall health and longevity.
Ready to take control of your dog’s weight? Stay tuned for our detailed guide on helping your furry friend achieve and maintain a healthy weight!
Critical Health Risks Associated with Obesity In Dogs
Dog obesity is more than just a cosmetic issue. Extra weight can drastically impact your furry friend’s health and quality of life. Understanding the health risks of overweight dogs is key for responsible pet owners who want to protect their canine companions.
Excess weight puts tremendous strain on your dog’s body, creating multiple serious health challenges. Let’s explore the critical overweight dog health risks that every pet owner should know!
Joint and Mobility Problems
Excess weight creates significant stress on your dog’s joints and skeletal system. The additional pounds can lead to:
- Increased risk of arthritis
- Reduced mobility and flexibility
- Chronic pain in legs and spine
- Higher likelihood of ligament and tendon injuries
“Every pound of extra weight is like carrying a heavy backpack for your dog’s joints!” – Veterinary Orthopedic Specialist
Cardiovascular Issues
Obesity dramatically increases the risk of heart-related problems. Overweight dogs often experience:
- Decreased heart efficiency
- Higher blood pressure
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Reduced exercise tolerance
Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders
Pet health tips always emphasize weight management because obesity directly impacts metabolic functions. Overweight dogs are more susceptible to:
- Insulin resistance
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hormonal imbalances
- Reduced metabolic efficiency
By understanding these health risks, you can take proactive steps to help your dog maintain a healthy weight. This way, your dog can enjoy a happier, more active life!
Identifying Signs of Obesity In Dogs
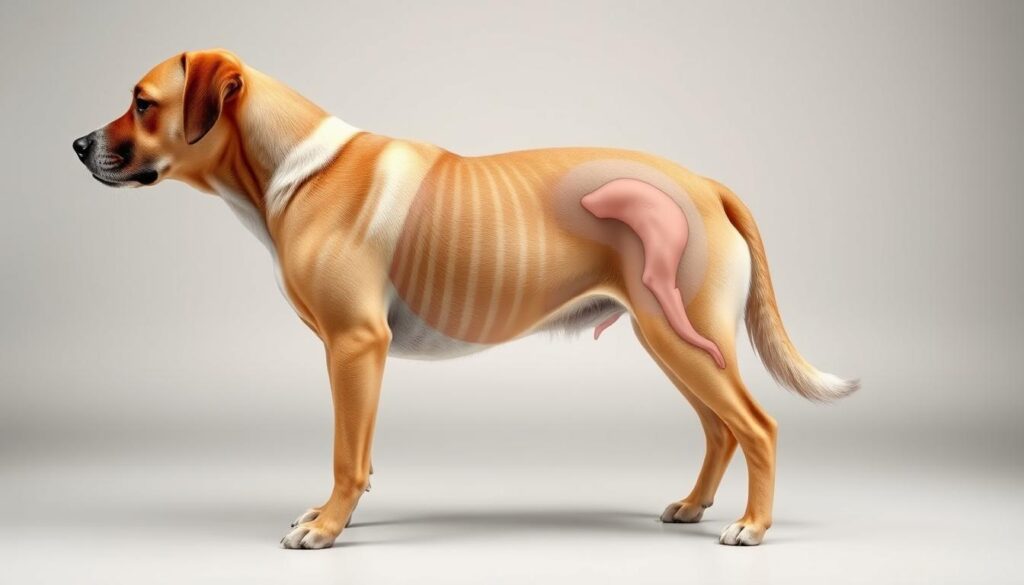
It can be hard to tell if your dog is overweight. Obesity in dogs is a serious health issue that needs careful watching and action.
Here are the main signs to look for to see if your dog might be obese:
- Difficulty feeling your dog’s ribs when gently touching their sides
- No visible waistline or abdominal tuck when viewed from above
- Reduced energy levels and decreased willingness to play
- Labored breathing during mild activities
- Noticeable fat deposits around the neck and base of the tail
Is your dog overweight? Look out for these extra warning signs:
- Decreased mobility or reluctance to move
- Weight gain without significant changes in diet or exercise
- Decreased muscle tone and overall fitness
Vets suggest using a body condition scoring system to check your dog’s weight. This method looks at your pet’s body and checks its structure to see if it’s at a healthy weight.
Early detection of canine obesity can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life and prevent possible health problems!
If you see these signs, don’t worry. With the right diet, exercise, and vet advice, you can help your dog stay at a healthy weight.
Common Causes Behind Dog Weight Gain Obesity In Dogs
It’s important to know why dogs gain weight. This knowledge helps us keep our pets healthy and prevent obesity. Dogs can gain weight for many reasons, and understanding these is key to managing their weight.
Overfeeding and Poor Diet Choices Obesity In Dogs
Many pet owners unintentionally cause their dogs to gain weight. Too many treats, table scraps, and high-calorie foods can lead to weight gain. Owners often struggle with:
- Misunderstanding proper portion sizes
- Frequent treat-giving
- Feeding low-quality commercial dog foods
- Lack of nutritional knowledge
Lack of Exercise
Busy lives can affect a dog’s exercise. Dogs need regular walks and playtime to stay healthy. Without enough exercise, they burn fewer calories and can become obese.
- Insufficient daily walks
- Limited playtime
- Indoor-only living environments
- Reduced physical stimulation
Medical Conditions
Some health issues can make dogs gain weight. Conditions like hypothyroidism and Cushing’s disease can slow metabolism or increase hunger. Other medical causes include:
- Hypothyroidism
- Cushing’s disease
- Insulin resistance
- Hormonal imbalances
Knowing these causes empowers pet owners to take proactive steps in managing their dog’s weight and overall health!
Creating an Effective Weight Loss Plan for Your Dog
Helping an obese dog lose weight needs a careful plan. Our expert guide will show you how to make a weight loss plan for your dog. This plan will help your dog become healthier and happier!
Creating a good weight loss plan for an obese dog involves several steps. Start by talking to your vet. They will help you make a plan that fits your dog’s needs.
- Consult with your veterinarian for a complete health check
- Set realistic weight loss goals
- Make a detailed nutrition plan
- Start a regular exercise routine
- Keep track of progress regularly
When using weight loss tips for dogs, make changes slowly. Losing weight too fast is not safe for dogs. Aim for a weight loss of 1-2% of body weight each week.
| Weight Loss Strategy | Key Actions |
|---|---|
| Nutrition Modification | Lower calorie intake, pick high-protein, low-fat foods |
| Exercise Plan | Boost daily activity, start with short walks, then increase time |
| Monitoring | Weekly weigh-ins, body condition scoring |
Remember, losing weight with your dog is a team effort. You, your pet, and your vet all play a part. Stay positive, consistent, and patient on this weight loss journey!
Pro Tip: Treats should make up no more than 10% of your dog’s daily calories during weight loss.
Proper Nutrition and Diet Modifications for Overweight Dogs
Creating a healthy diet for overweight dogs needs careful planning. Obesity can cause serious health issues. So, a good diet plan is key for their health and long life.
For weight loss, focus on two main things: portion control and choosing the right food. Your dog needs a balanced diet for slow, steady weight loss.
Calculating Proper Portions
Finding the right food amount is vital for weight control. Consider these important factors:
- Current weight and ideal target weight
- Age and activity level
- Metabolic rate and overall health condition
Choosing the Right Dog Food
Pick a high-quality, low-calorie dog food made for weight management. Look for foods with:
- High protein content
- Low fat percentage
- Essential nutrients and vitamins
| Food Type | Calories per Cup | Protein Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Management Kibble | 260-320 | 25-30% |
| Regular Adult Dog Food | 350-400 | 18-22% |
Healthy Treats and Alternatives
Swap high-calorie treats for low-calorie, nutritious ones. Good choices include:
- Carrot sticks
- Green beans
- Small pieces of cooked chicken breast
- Commercial low-calorie dog treats
Remember: Successful weight loss is a journey of consistent, mindful nutrition and patience!
Exercise Strategies for Obese Dogs
Helping your overweight dog lose weight needs a careful plan. Start by understanding your dog’s fitness level. Then, create a safe, gradual exercise routine.
Begin with low-impact activities to avoid hurting your dog’s joints or heart. Short, gentle walks are great for dogs starting their weight loss. Start with 5-10 minute walks and increase as your dog gets stronger.
- Swimming: An excellent low-impact exercise that burns calories without stressing joints
- Short walks around the neighborhood
- Gentle play sessions with interactive toys
- Indoor games that encourage movement
To help your dog lose weight through exercise, make activities fun and engaging. Use interactive toys like puzzle feeders or slow-moving fetch games. This makes exercise enjoyable and prevents boredom.
Remember: Always consult your veterinarian before starting any new exercise program for an overweight dog!
Water-based exercises are great for dogs with mobility issues. Many vet centers have underwater treadmills for canine weight loss.
As your dog gets fitter, increase the exercise intensity. Watch for signs of improvement like more energy, better breathing, and increased mobility. Being consistent is essential for a successful dog exercise routine!
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting the Weight Loss Plan
Tracking your dog’s weight loss is key to success. Our approach helps you keep up with your pup’s progress. This ensures they reach their health goals safely and effectively.
Regular monitoring lets you tweak your weight loss plan. Let’s look at the main ways to track your dog’s progress!
Weekly Weigh-ins: Your Progress Checkpoint
Regular weigh-ins are vital for managing your dog’s weight. Here’s how to track:
- Use the same scale each time
- Weigh at the same time of day
- Record weight in a consistent log
- Aim for weekly measurements
Body Condition Scoring System
Body condition scoring gives a full view of your dog’s weight loss. It’s a visual and tactile way to see physical changes.
| Body Condition Score | Physical Characteristics | Weight Management Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 (Underweight) | Ribs visible, no fat cover | Increase calorie intake |
| 4-5 (Ideal Weight) | Ribs felt easily, waist visible | Maintain current diet and exercise |
| 6-9 (Overweight/Obese) | Thick fat cover, no waist definition | Reduce calories, increase exercise |
Exercise Tolerance Assessment
Watching your dog’s exercise capacity is important. Look for signs of better endurance and energy during activities.
- Track walking/play duration
- Note recovery time after exercise
- Observe overall enthusiasm for movement
- Gradually increase exercise intensity
Every dog’s weight loss journey is different. Be patient, consistent, and always check with your vet. This way, you can make the best weight management plan for your furry friend.
Breeds Prone to Obesity and Special Considerations
Some dog breeds are more likely to gain weight. This is because of their genetics and lifestyle. Knowing about dog obesity can help owners prevent it in different breeds.
Some breeds are at higher risk of getting overweight. This is because of their unique traits. To prevent canine obesity, owners need to pay extra attention to these breed-specific challenges.
- Basset Hounds: Known for low activity levels and slower metabolism
- Beagles: Extreme food motivation and tendency to overeat
- Border Terriers: Prone to weight gain with reduced exercise
- Boxers: Muscular breed with a risk of rapid weight gain
- Bullmastiffs: Large size combined with lower energy levels
Genetics play a big role in dog obesity. Some breeds have traits that make it harder to manage their weight. Their body type, metabolism, and appetite can lead to weight problems.
Understanding your dog’s breed-specific characteristics is key to maintaining a healthy weight!
It’s important to work with vets to create a weight management plan. Each breed needs a specific diet and exercise plan to stay healthy.
By knowing the breed-specific challenges, owners can take targeted steps to prevent obesity. Regular checks, the right food, and consistent exercise are key to keeping your dog healthy.
Maintaining Healthy Weight After Weight Loss
Congratulations on helping your furry friend reach their weight loss goals! Dog weight management doesn’t end after reaching the target weight. It’s key to keep a healthy diet to avoid dog obesity in the long run.
Switching from a weight loss plan to a maintenance routine needs a good plan. Your vet can guide you on the right calorie intake and nutrition for your dog’s needs.
- Monitor portion sizes consistently
- Continue regular exercise routines
- Schedule periodic weight check-ups
- Adjust diet as your dog ages
Important strategies for avoiding dog obesity include:
| Strategy | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Daily Exercise | 30-60 minutes of moderate activity |
| Portion Control | Measure meals precisely |
| Treat Management | Limit treats to 10% of daily calories |
Remember, dog weight management is a lifelong commitment. Regularly check your dog’s body condition, adjust their diet when needed, and keep up with exercise. Your hard work will keep your furry friend healthy and lively!
“A healthy dog is a happy dog – and prevention is always better than cure!”
Dogs Prone to Obesity (Including Some of the Fattest Breeds)
Several dog breeds are genetically predisposed to obesity due to their lower activity levels, passion for food, and genetic factors. Some of the fattest dog breeds include:
1. Basset Hound
- Inherited Genetics: Prone to weight gain due to genetic factors.
- Passion for Food: Very food-driven, often begging for treats.
- Low Activity Levels: Basset Hounds are not the most energetic breed, preferring to relax.

2. Beagle
- Inherited Genetics: Beagles are naturally inclined to gain weight.
- Passion for Food: Their keen sense of smell leads them to be highly food-oriented.
- Low Activity Levels: While active, they often have periods of lower energy, especially if not motivated to exercise.

3. Border Terrier
- Inherited Genetics: Border Terriers may struggle with weight if not managed carefully.
- Passion for Food: Known for their love of food, which can contribute to overeating.
- Low Activity Levels: Not the most active breed, needing encouragement for regular exercise.

4. Boxer
- Inherited Genetics: Boxers can easily gain weight if not properly managed.
- Passion for Food: They love food, which can lead to overeating if not controlled.
- Low Activity Levels: Boxers are active but can also have lazy moments.

5. Bullmastiff
- Inherited Genetics: Bullmastiffs are prone to weight gain due to their genetics.
- Passion for Food: They love food and are known to eat heartily.
- Low Activity Levels: They are generally more relaxed and less active compared to some other breeds.

6. Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
- Inherited Genetics: This breed is prone to obesity due to its genetic predisposition.
- Passion for Food: Cavalier King Charles Spaniels love food and are often seen begging for treats.
- Low Activity Levels: They have lower energy levels and prefer lounging around.

7. Chihuahua
- Inherited Genetics: Chihuahuas can gain weight easily if not monitored.
- Passion for Food: They are food-driven and tend to overeat if allowed.
- Low Activity Levels: Chihuahuas are not known for being very active.

8. Cocker Spaniel
- Inherited Genetics: Cocker Spaniels can gain weight easily if overfed.
- Passion for Food: They enjoy food, which can contribute to overeating.
- Low Activity Levels: Though energetic, they can be lazy without proper exercise.

9. Corgi
- Inherited Genetics: Corgis have a tendency to gain weight due to their body structure.
- Passion for Food: Known for their love of food.
- Low Activity Levels: Corgis are generally playful but can become inactive if not regularly stimulated.

10. Dachshund
- Inherited Genetics: Dachshunds are prone to obesity due to their compact bodies.
- Passion for Food: They have a big appetite and love eating.
- Low Activity Levels: Despite their small size, Dachshunds can be quite sedentary.

11. English Bulldog
- Inherited Genetics: Bulldogs are genetically prone to weight gain.
- Passion for Food: They are food-lovers and will often overeat.
- Low Activity Levels: Bulldogs are known for their calm and laid-back lifestyle.

12. French Bulldog
- Inherited Genetics: French Bulldogs are naturally inclined to gain weight.
- Passion for Food: Their love for food can lead to overeating.
- Low Activity Levels: French Bulldogs tend to be more sedentary.

13. German Shepherd
- Inherited Genetics: German Shepherds may gain weight if not properly exercised.
- Passion for Food: They enjoy food, especially high-protein treats.
- Low Activity Levels: While generally active, German Shepherds can become overweight if not exercised regularly.

14. Golden Retriever
- Inherited Genetics: Golden Retrievers are prone to obesity if not watched carefully.
- Passion for Food: They love food and will often eat anything they are given.
- Low Activity Levels: Golden Retrievers are naturally active but can gain weight without enough exercise.

15. Labrador Retriever
- Inherited Genetics: Labradors have a genetic tendency to gain weight.
- Passion for Food: They have a very strong food drive.
- Low Activity Levels: While energetic, Labradors can become overweight if not exercised properly.

16. Newfoundland
- Inherited Genetics: Newfoundland dogs are prone to obesity due to their large size and genetics.
- Passion for Food: They enjoy food and are easy to overfeed.
- Low Activity Levels: While strong swimmers, they are generally calm and less active on land.

17. Pit Bull
- Inherited Genetics: Pit Bulls can gain weight easily due to their muscle structure.
- Passion for Food: They have a high appetite and love eating.
- Low Activity Levels: Though active, they can become lazy if not consistently stimulated.

18. Pug
- Inherited Genetics: Pugs are prone to obesity due to their small size and appetite.
- Passion for Food: They love food and are quick to beg for treats.
- Low Activity Levels: Pugs have a laid-back lifestyle, which can lead to weight gain.

19. Rottweiler
- Inherited Genetics: Rottweilers are prone to gaining weight due to their body type.
- Passion for Food: They love food and are very food-driven.
- Low Activity Levels: Rottweilers are active but can become overweight if not regularly exercised.

20. Scottish Terrier
- Inherited Genetics: Scottish Terriers can be prone to obesity.
- Passion for Food: They are food-driven and will eat anything they can.
- Low Activity Levels: Scottish Terriers tend to be less active.

21. Shar Pei
- Inherited Genetics: Shar Peis can gain weight easily.
- Passion for Food: They enjoy food, often leading to overeating.
- Low Activity Levels: This breed is generally laid-back.

22. Shetland Sheepdog
- Inherited Genetics: Shelties may gain weight due to their genetics.
- Passion for Food: They enjoy food and will often eat quickly.
- Low Activity Levels: Though energetic, they may not be as active without proper stimulation.

23. Shih Tzu
- Inherited Genetics: Shih Tzus can easily gain weight if not properly managed.
- Passion for Food: They are food-driven and love treats.
- Low Activity Levels: Shih Tzus are generally low-energy dogs.

24. Staffordshire Bull Terrier
- Inherited Genetics: Staffordshire Bull Terriers may gain weight if not exercised enough.
- Passion for Food: They are highly motivated by food.
- Low Activity Levels: Though strong, they can be sedentary.

25. West Highland White Terrier
- Inherited Genetics: Westies are prone to gaining weight.
- Passion for Food: They love food and often beg for it.
- Low Activity Levels: While energetic, they can be sedentary without enough stimulation.

Conclusion
Managing canine obesity is a journey filled with love and commitment. Our guide has covered the key aspects of dog weight management. It offers vital pet health tips to ensure your furry friend’s well-being.
Understanding the risks and how to tackle weight issues can greatly enhance your dog’s life. This journey is not simple, but it’s very rewarding.
By using the nutrition, exercise, and monitoring tips we’ve shared, you can help your dog reach and keep a healthy weight. Canine obesity is a serious issue, but with the right effort, you can make a big difference for your pet.
Every dog is different, and managing their weight needs patience, consistency, and expert advice. Veterinarians are your go-to for advice that fits your dog’s needs. Your dedication to your pet’s health is key in fighting weight-related problems.
Start this wellness journey with excitement and care. Your dog relies on you to make choices that support their health and happiness. Together, you can beat obesity and enjoy a happy, active life full of joy and wagging tails!
How to Use a Bike and Dog Leash for Safe Exercise
FAQ
Q: How do I know if my dog is overweight Obesity In Dogs?
A: Check if your dog is overweight by feeling their ribs and looking at their waistline. Watch for signs like less energy and trouble moving. A vet can do a body condition score to check your dog’s weight.
Feel your dog’s ribs without a thick layer of fat. They should have a visible waist when viewed from above.
Q: What health risks are associated withObesity In Dogs?
A: Obesity in dogs can cause serious health issues. These include joint problems, heart diseases, diabetes, and a shorter life. It also affects their breathing and quality of life.
Extra weight strains their organs and limits their daily activities and long-term health.
Q: How can I help my dog lose weight safely Obesity In Dogs?
A: To help your dog lose weight safely, talk to your vet for a weight loss plan. This plan might include eating less, measuring food, and choosing a special diet. It also includes more exercise and fewer treats.
Remember, weight loss should be slow, about 1-2% of body weight each week.
Q: What causes obesity in Obesity In Dogs?
A: Obesity in dogs can come from many things. These include eating too much, not exercising enough, and poor diet choices. Too many treats and certain breeds are also factors.
Owners often unintentionally help their dogs gain weight by giving too many calories and not enough exercise.
Q: How much exercise does an overweight Obesity In Dogs need?
A: Start with short, gentle walks and gradually increase the time and effort. Aim for 15-30 minutes of daily activity. Swimming, controlled walks, and interactive play are good options.
Always talk to your vet to create a safe exercise plan for your dog.
Q: Are certain dog breeds more prone to Obesity In Dogs?
A: Yes, some breeds are more likely to gain weight. These include Basset Hounds, Beagles, Bulldogs, Pugs, and Labrador Retrievers. They might have slower metabolisms or need more exercise.
But, with the right diet and exercise, these breeds can stay healthy.
Q: How often should I weigh my dog during weight loss?
A: Weigh your dog every 2-4 weeks during weight loss. This helps track progress without focusing too much on daily changes. Your vet can help set up a weighing schedule and explain the results.
Q: What are some low-calorie treat alternatives for Obesity In Dogs?
A: Healthy, low-calorie treats include carrot sticks, green beans, and small pieces of cooked chicken. You can also use specially made low-calorie dog treats. Always introduce new treats slowly and in small amounts.
These alternatives can help satisfy your dog while they lose weight.




Pingback: Discover Stylish And Comfortable Extra Large Dog Apparel - The Pet Advisor